#Roman Emperors
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

188 notes
·
View notes
Text
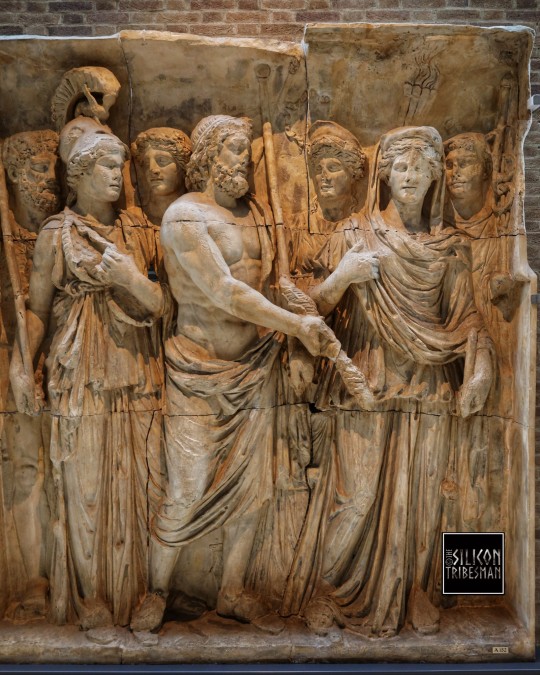
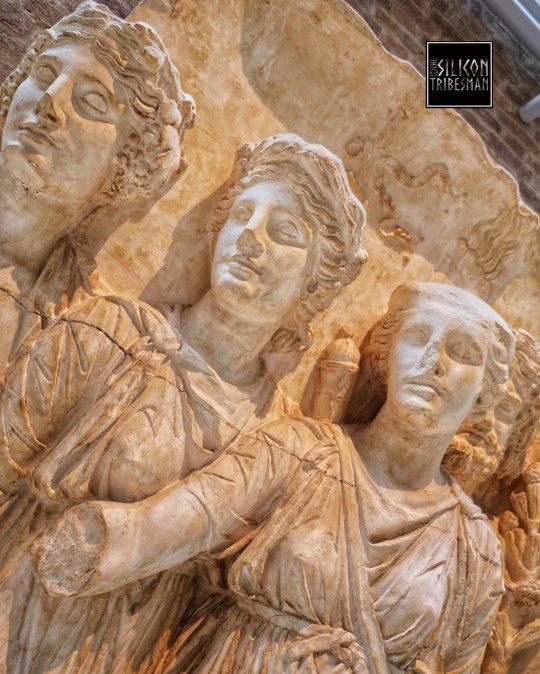



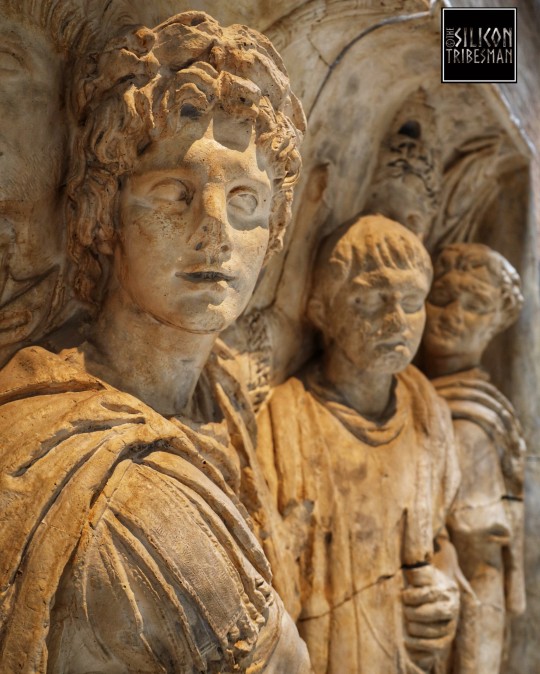
Roman Gods And Goddesses of the Countryside, Arch of Trajan at Beneventum, 114 CE
These gods and goddesses represent the prosperity of the countryside: Bacchus, god of the vine with his thyrsos (a fennel-stalk staff); Ceres, goddess of corn and the harvest, with a torch; Diana, goddess of hunting and wild animals; and Silvanus, god of woods and fields, who holds a pine branch (in situ, west side, attic).
Ashmolean Museum, Oxford
#roman gods#roman goddess#roman deities#roman belief#roman villa#roman farms#roman countryside#countryside#nature#seasons#roman emperors#roman living#roman empire#ro.an sculpture#trajan#archaeology
416 notes
·
View notes
Text
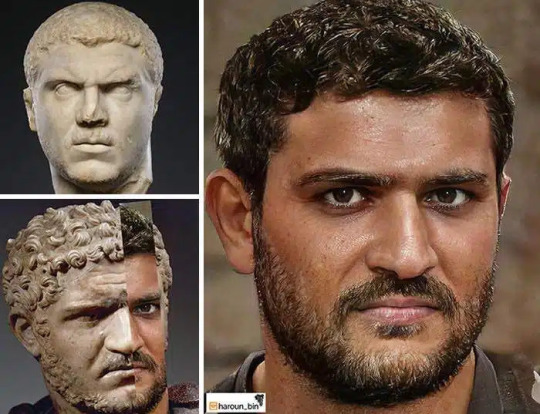

The enigmatic emperor Caracalla. Lucius Septimius Bassianus, renamed Marcus Aurelius Antoninus at age 7, was born on April 4, 188 in Lugdunum, Gaul (Lyon, France). Like 'Caligula', he's known by a nickname rather than his name.
His father, Septimius Severus, became the first Roman emperor of North African origin in 192; His mother, Julia Domna, was a noble lady of Arab origin born in Emesa (Homs, Syria)
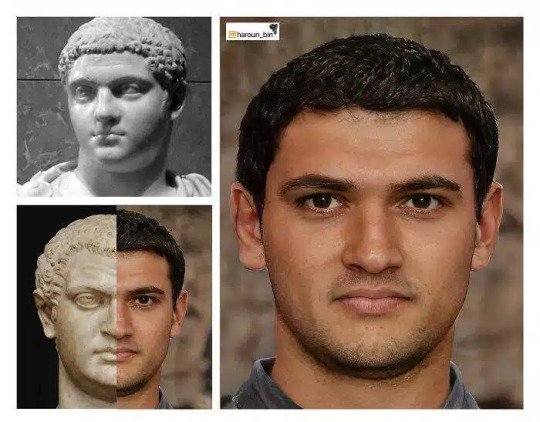

Publius Septimius Geta was born in Rome, 11 months after his brother 'Caracalla'. All historical sources claim that they never had a brotherly relationship. According to historians, Geta was more appreciated by the Senate and the people than his brother. Herodian wrote that they constantly fought for any reason and "it was impossible to hide the rivalry between the brothers, although the emperor Septimius tried in vain to keep this from being known".

"Geta and Caracalla" by Sir Lawrence Alma Tadema (detail). In this painting the Emperor Septimius and the Empress Julia Domna are shown seated. Geta is standing next to a woman, and Caracalla is pensive by a column; the painter depicts him as sad - perhaps jealous - of his brother's popularity.
An unusual empress
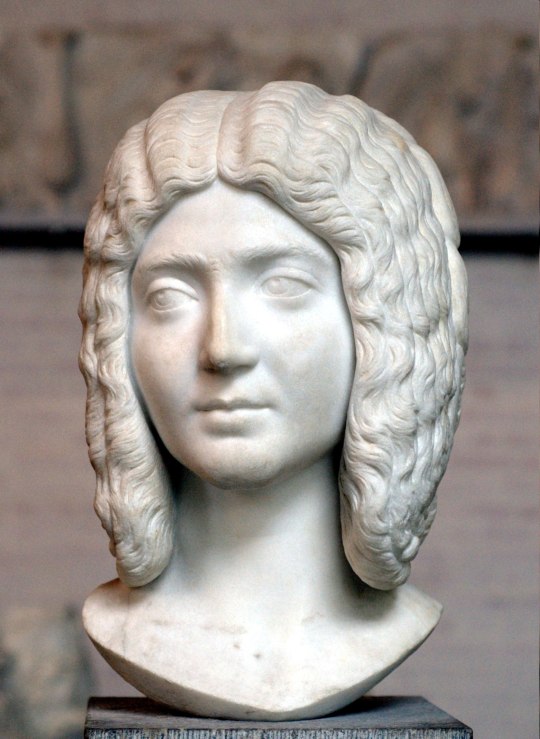
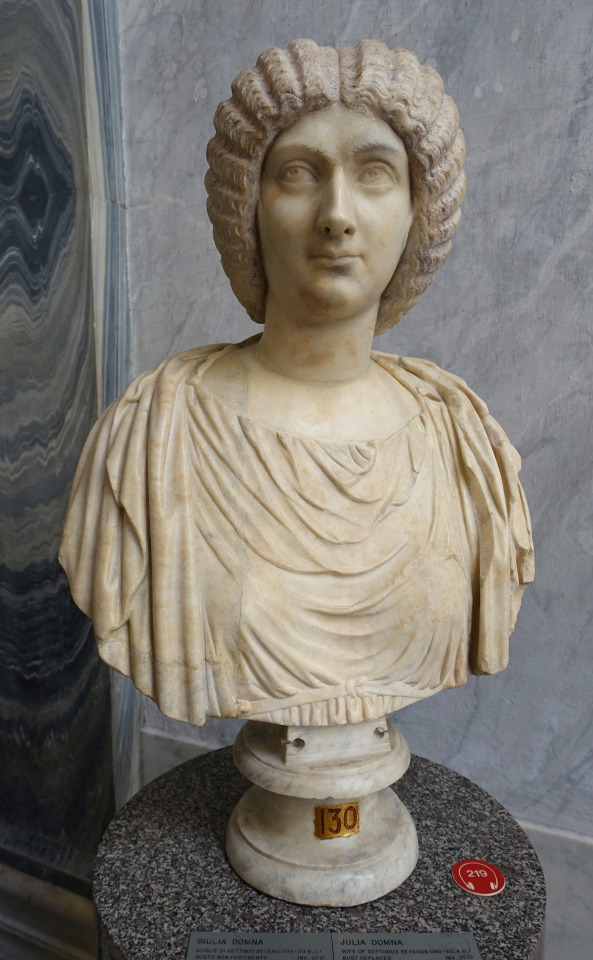


Busts of Julia Domna. Photos :Bibi Saint-Pol, and Daderot (CC)
Julia Domna always accompanied her husband in all the campaigns, the reign of Septimius Severus was extremely militarized. She received the title Mater Castrorum (Mother of the legionary camps). She made political decisions directly, something unprecedented in Rome for a woman. After the death of Septimius, Julia Domna was granted the titles: Mater Senatus and Mater Patriae (Mother of the Senate, Mother of the Nation). She was a scholar in Philosophy, and had a notable influence on that subject. She was involved in several architectural projects including the famous Caracalla Baths, enormous work planning by her husband and completed by her son. She was highly respected by the Senate throughout her reign (192-217).
"Let there be peace among you both, pay the army well and forget the rest". -Septimius Severus to his children on his deathbed

'Geta Dying in his Mother's Arms' by Jacques Pajou.
Britannia, February 4, 211: Septimius died of natural causes, accompanied by his family. Caracalla and Geta, aged 22 and 21, had been emperors with their father since childhood, but after the death of Septimius, as expected, such co-government would not last long.
According to contemporary historian of that period, Herodian : "The co-emperors constantly quarreled and feared that one of them would poison the other, so they did not eat at the same table."
Rome, December 27, 211: 'Caracalla' ordered the execution of Geta, claiming to have discovered that his brother was plotting to assassinate him. The execution carried out by two centurions was in the presence of Julia Domna. According to contemporary sources, Caracalla had tried to kill Geta a few days earlier, during the Saturnalia festival.
Following Geta death he ordered the execution of all Geta's supporters, among them Lucius Aurelius, the only grandson of Marcus Aurelius, son of Lucilla and Pompeianus.
The curious thing is that empress didn't leave her son Caracalla; This caused the Empress to lose popularity among the people, especially in the eastern provinces where, according to historians, Geta was very popular.
If you were born in Roman territory so you're a Roman.

In 212 he issued the Constitutio Antoniniana, also known as the Edict of Caracalla, which granted Roman citizenship to every free men and women living in Roman territory - although by then Roman citizenship had increased significantly throughout the empire - and from then on every free child born in the Empire was a Roman. This was criticised by contemporary historians but modern historians agree that he understood what certain elitist people in the city of Rome refused to understand. 'Caracalla' was Emperor of Rome but he was of Punic and Arab origin and born in Gaul; he was living proof that the city of Rome was the capital of a multi-ethnic world.
An awesome site



Baths of Caracalla. Reconstruction made by team of 'History in 3D'
The Caldarium (sauna) was built in the Pantheon style and the vestibule was in basilica style; Just two simple parts of a baths building were something magnificent in themselves. It was an immense complex that, in addition to the typical cold, warm, and hot baths, dressing room, massage and beauty salons, included two libraries, gym, impressive swimming pools, a stadium , vast gardens, a small museum with exhibitions of works of art, and a shopping center with a wide variety of businesses.
The Alexandria Massacre

'Caracalla' by Sir Lawrence Alma Tadema
After a trip through the eastern provinces, in December 215 he arrived in Alexandria. The Alexandrians, outraged by the death of emperor Geta, began to public perform plays of satire mocking Caracalla and in which they called empress mother "Jocasta." According to the famous legend, Jocasta was the mother of Oedipus who, after killing his father, had married his own mother. Upon discovering this his wrath was such that ordered a massive executions. Caracalla attacked the city with his troops for several days, in a kind of personal war against Alexandria.
Unexpected death
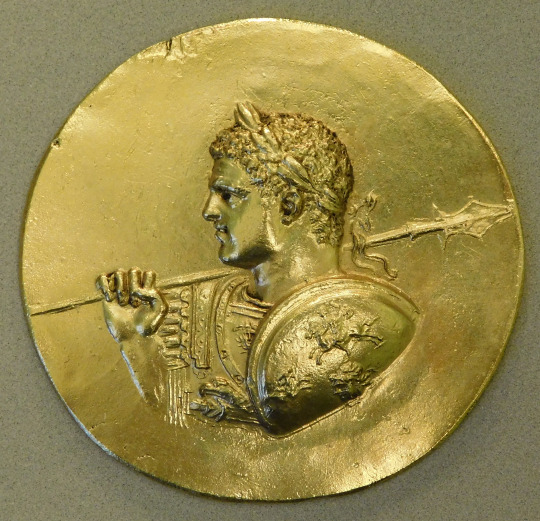

Gold medal bust of Caracalla with the shield of Alexander the Great. By Sailko /CC BY 3.0 /wikimedia commons.
In 216 he offered King Artabanus IV of Parthia to marry his daughter, but the king rejected the offer. Caracalla took advantage of this "snub" to start a campaign against the Parthian empire. He began attacking the countryside east of the Tigris. In early 217 he was in Edessa (modern Şanlıurfa,Turkey) preparing to restart the campaign.
On April 8, 217, four days after his 29th birthday, he was traveling to a temple near Carras (Harran, southern Turkey) and when he stopped to urinate, the praetorian soldier Martialis assassinated him with his sword. According to historical sources, the Prefect of the Praetorian Guard, Macrinus commissioned him to assassination. Martialis was executed immediately after Caracalla's death, and three days later Macrinus proclaimed himself emperor.
Empress Julia Domna was in Antioch, upon learning of the assassination decided to take her own life.
This seems like the end of The Severan dynasty, however it wasn't. Julia Maesa, older sister of Julia Domna, was a strong lady.
In her hometown, Emessa, where Macrino had forced her to return, she took advantage of the fact that it was a place with an important military base. She organized with the legions a war against the usurper Macrinus. She placed his grandson Elagabalus on the throne on May of 218. Macrinus, who had fled to Cappadocia, was executed two months later. After the death of Elagabalus, the other grandson of Julia Maesa, Alexander Severus, ruled until 235.
"I know that none of you like what I do, that's why I have weapons and troops: so that at no time do I have to worry about what you say about me." -Caracalla to the Senate
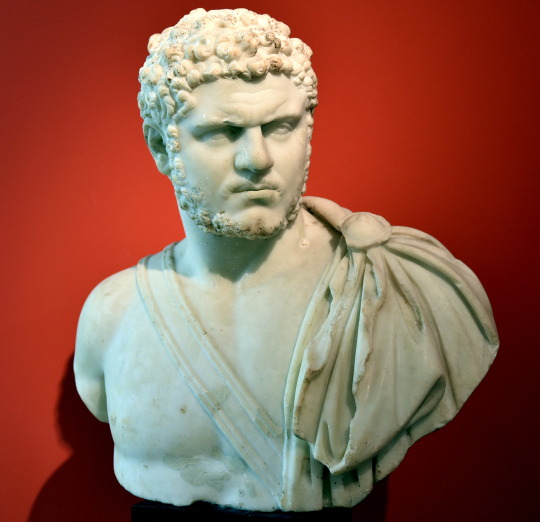

Emperor Caracalla. Marble. Acquired from Rome, Italy, in 1875. Altes Museum, Berlin. Photo: Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP (Glasg) CC BY-SA 4.0- Wikimedia Commons
He is known as 'Caracalla' because that is what the Romans called a Gallic garment with a hood that they say this emperor didn't take off even to sleep.
344 notes
·
View notes
Text
“How often do you think about the Roman Empire?”



Constantly.
173 notes
·
View notes
Text

𝒞𝓊𝓇𝓈𝑒𝒹 𝒷𝓎 𝒯𝒽𝑒 𝒢𝑜𝒹𝓈

CHAPTER 1: 𝔗��𝔢 𝔅𝔯𝔬𝔱𝔥𝔢𝔯𝔰' 𝔗𝔞𝔩𝔢
Prologue's here !
Caracalla x female!OC x Geta
Summary:
How did the Emperors gain power? What was their past like? What made Caracalla a madman?
Lucia Galeria Aurelia is the forgotten daughter of Lucilla and Maximus. One day her life changes forever when her path crosses with the young Caracalla. She starts to take an active part in the life of Rome, captivating not only the Roman people but also someone fate condemned her to - certain red-haired rulers.
Warnings: english is not my first language(!), alluding to sex, suicide, mentions of concubines, alcohol, swearing
AN: I really dig through history with this one. One of Severus's quotes he actually told in real life, not gonna spoil it tho!
Trope: enemies to lovers (duh)
Word count: 2.9k

At night, the two young people were led to a large chamber, unlike the one little Lucia was used to. It was an almost-hall, which had been the chamber of imperial marriages since the time of Nero, with large windows and a beautiful vault depicting Eros leaning towards Psyche, who sees her husband for the first time, with fear and uncertainty but also love painted on her face. Something that Lucia wanted to feel very much. She thought quickly, on their way to the chamber she managed to imagine the next years, the future of Rome, which she had to start taking care of. She glanced at her new husband's father from one side and at her mother from the other. She did not look past her, even though she felt the eyes of everyone following her, 'guiding' the newlyweds to their wedding night. She felt bad, the worst. She could only look at the back of her husband, who was walking in front of her, he had a certain posture and broad shoulders, but there was something funny about him, too funny. She tried to find the humor in the situation, she smiled to herself. “That’s my husband,” echoed in her head. They stopped. Two praetorians and Severus entered the chamber. In the middle stood a large bed with silk sheets and velvet pillows on which lay the heads of great rulers. Lucia wondered if all the young Roman brides felt as she did.
-Listen, young ones - Severus broke the deathly silence - Today you begin your marriage. You also start to play your role, as husband and wife, emperor and empress, woman and man. The gods gave you the ability to give life. You are here because it was given to you, and you should not end it without giving it to the next generation. Such is your task.
Only now could the girl see the true, obsessive face of the ruler of Rome. A ruler who knew that his days were numbered, a ruler who wanted his family to survive, more than anything in the world. Even if he had to sacrifice his son's happiness, sacrifice himself. He wanted everything to happen quickly, preferably here and now. The strange thing was that Lucia was not afraid. She was not afraid of this older, red-haired man, who, despite the large wreath and the storm in his pupils, was not dangerous to her at all. He looked almost pathetic to her, his desperate efforts to keep the throne. But only to her did he look like that. When she looked to the side, the purest form of fear was drawn on her husband's face. Maybe it was because his father had his eyes fixed on him the whole time, as if the future of Rome, the world, rested on his shoulders. His lips, still slightly stained with the cherry color of Lucia's lip cream, trembled before that stern look.
- Do you understand, son? - he asked, grabbing the young man’s hair - Now is your time for this. You will give me a descendant of your own blood, you will maintain our family, right, son? - he pierced his son with his gaze, who could only nod slightly.
As he left, he locked them in the room alone, probably leaving the praetorians behind them. For the first time, she could talk to him. She opened her mouth hastily, but he did the same at that moment.
- Let's just get this over with - she whispered as they sat on either side of the bed. It took some time before she took off her tunic, stola, and palla. When she did, only her long curls, shimmering in the light of the sad moon, fell on her body. After a long, rather awkward moment, she touched his fettered face a little timidly. Caracalla was afraid, afraid of his father, afraid of Rome and afraid of power. Although he was never really afraid. Even during the wedding, he was not afraid, he was angry. Pissed to the bone, he devoured his barbarian father with his eyes, imagining him on the noose. His father, his whole life, had not treated him like this. He felt betrayed. Looking at his beautiful wife, he felt only regret. He only nervously bit his cherry lip, the color of which mixed with blood. She took his face in both hands as if she wanted to wake him up from this trance of emotions.
- Just do it, Geta - she whispered, hugging him
- Geta..? - his first word since the wedding rang out
- Just do it!
- I’m Caracalla!
- What? - she stopped the embrace to look at him
- Caracalla the Gladiator?
- What? - he said like an echo
- Geta was supposed to be the emperor..
- What are you talking about..
After another long moment of looking at each other, the girl burst into uncontrollable laughter. Caracalla, surprised by the whole situation, expressed perhaps a shadow of amusement, but with his whole body confusion. How could he possibly know how the girl found out about the twin rulers?
A while earlier, one day when she first snuck out of the chamber and found Macrinus, he showed her the gladiators' weapons. He presented her with each item and she absorbed the knowledge like no one else. She wanted to take one of the smaller swords, for warriors of smaller stature, but there were none. Maybe because of adversity, maybe because young Caracalla stole swords for his chamber, swords that probably fascinated him as much as Lucia.
- Sorry, kid. It seems like another young gladiator was faster than you. This little, red-haired one, Caracalla. I'm telling you, when I live to see his reign, I'll give myself freely to the hands of the Gods - Macrinus told her, laughing.
Lucia had heard stories about people waiting for a new ruler, who was supposed to be Geta. They hoped that he would end the tyranny and break the curse of his family. Maybe she believed in those fairy tales and maybe that was why she was so calm.. Until she found out that it wasn't her husband.
The laughter died down a bit, the boy continued to look at her with a blank stare, as if begging her to leave him alone or at least explain what was going on.
- Do you even want to be an emperor?
- Not with an empress like you.
- Ouch, spare me Geta - her innate cynicism was revealed for the first time as she leaned back on the pillows with playful eyes, now in all her glory as a beautiful empress. Caracalla was calmer, his fear diminished when he noticed he had no enemy in her. For the first time, he smiled, showing his teeth, some gleaming gold.
- Where did you even come from?
- I hatched from a shell like Venus - she giggled, stretching.
- Fair enough..
There was silence again for a moment. Caracalla liked to stare, piercing everything with his gaze. He looked silly to her, maybe even sweet. She wasn't sure if he had the face of the future emperor. They looked at each other, she turned her head slightly to the side, for the first time she actually saw him, without the shadow of his tyrannical father, just him, the 18-year-old boy Caracalla. After all, they were in this together.
- So…What’s it like to have.. a brother?
- I dunno.. I guess good, as long as your wife doesn't confuse you with him - the echo of a boyish chuckle spread through the large room. Lucia was curious about this, she had never met any peers, only heard once or twice about her brother, who was alive, but not present. Who probably didn't know that there was someone like her, someone who wanted to see him more than everyone else. The girl wanted to feel at least a drop of brotherly love, to hear about it.
- No, I'm serious. Do you love him?
- We do everything together. I'm condemned to him like.. To you
- Condemned? He's your only brother! - Her gaze was fixed on his now-turned head. A moment earlier they had covered themselves in their marital robes, the future emperor now curled up on the large bed, hiding his face in his hands. The girl probably wouldn't understand what he was feeling, even after reading all her grandfather's philosophical books and using up all of her intelligence.
- Don't you understand that I'm standing in his way? He won’t admit it, but it's true. I'll give you a child and he'll get lost in the shadows, forgotten. Do you understand? He's so.. good. An ideal emperor.
Caracalla was a child whose exceptionalism was acknowledged from an early age. People criticized him for his ridiculous attitude, but they admitted that he had bravado. Bravado that an emperor needed. The boy was not virtuous, he was against all virtues. He admired Commodus, Alexander the Great, heck, he ordered his statue to be placed in his room, he ordered a sword to be forged for himself with the date of the Macedonian ruler’s birth and death. Caracalla absorbed the history of wars and empires, he wanted to fight. When he was ridiculed for his small stature, his brother used to step in. Their relationship was, however, changeable, beyond understanding. Geta felt every resentment towards his brother, one could say from birth, for being the first to emerge from his mother's belly, for always being the first for no reason. Caracalla always had a certain difficulty with emotions. His love was obsessive, it came in waves, randomly. It changed. He couldn't talk about it. He was healthy his whole life, he didn't struggle with any illnesses, unlike his father. That was one of the reasons his father chose him as emperor, an ideal tyrant, leading conquests, winning wars. However, Caracalla fell into a spiral of debauchery. Wine and concubines tempted him from childhood. Maybe because his father surrounded himself with them all the time, and convinced him that he was an authority. Women could give the old emperor the power that he felt he was losing. Power over his sickly body, power over Rome.
Her warm breath tickled his ear. She embraced him, what a strange feeling. He never wanted pity, he didn't want to feel weak.
- I’m..
The door to the chamber was opened. A sonorous voice could be heard.
- You’re a noble pair, dear brother and sister. You look.. truly serious
Indeed, their faces did not express the bliss that the wedding night was supposed to bring. Lucia moved away from her husband, quickly and silently dressing. The tension was clearly felt between the brothers.
- Geta…
- Caracalla!
The taller red-haired boy with funny eyeliner embraced his brother in his marital robe, kissing him on the forehead. The kiss seemed brutal, full of brotherly rivalry. Everyone except Lucia guessed that this rivalry was about her. The moment of silence between the brothers looking at each other was interrupted by the praetorian entering.
- The emperor invites the couple for breakfast.
- That's what I wanted to tell you - Geta replied, watching Lucia dress from the side - the night passed quickly, didn't it?
Caracalla nodded again in a way she knew. It seemed the only thing that was weighing on him was the matter of this marriage. It looked like she had awakened an unusual side of him that no one but her had seen.
✦ ⎯⎯ㅤִㅤ୭ ୨♡୧ ৎㅤִ ⎯⎯ ✦
The table was huge, filled with all sorts of wild dishes, in honor of the newlyweds everything was soaked in wine, both bread and roast, and finally large carafes of drinks were brought which sparkled as poured into large goblets. Two places of honor at the end of the table were waiting for the young couple. All eyes were turned towards them, waiting for the feast to begin. Lucia also waited for Caracalla to stand up but his eyes wandered over individual people, not focused on the current moment. He leaned towards his brother to whom he whispered something. Geta waved his hand and patted him rudely on the shoulder. The boy stood up together with his wife, biting a piece of wine bread made of wheat as a sign to start the feast. Conversations immediately drowned out the solemn silence of the Golden House, you could hear a roar of clinking glasses and eating, laughter and shouting. The only people who seemed to be absent were, of course, the newlyweds. Lucia said nothing but listened attentively. Next to her sat Macrinus with the Senate, telling the wildest stories from the arena.
- Rome has something that the Egyptians, the Persians, and the Hindus have not achieved. We have a great Colosseum and games. We have honorable men for whom fighting is life, devoted to Ares, loyal to the Thunderer. Barbarians will never achieve what Rome has, we are the nation closest to the fullness of life, Socrates can laugh in his grave as much as he wants, but it is true.
- But aren't these honorable men brought from barbarian nations, from far across the sea? - a soft female voice broke through the applause of the older men, for a moment as if deafened by her interference.
- These matters should not bother your noble head in any way, dear Lady, I am sure that..
- She is right, Marcus, they are not Romans. That is why my task is to convert and train them, which as you can see gives me so much remuneration that today I am sitting right next to the future empress. - Macrinus interrupted the senator with a certain smile, glancing into the eyes of the clever Lucia.
On the other side of the table, however, the conversation was not going so smoothly. Caracalla was as nervous as ever. The pink powder on his cheeks was nothing compared to the blushes on his face, the blushes of anger and shame.
- Where the fuck is he? Isn't it time for one of his damned speeches? Besides, he’s sick as hell!
- He is celebrating in a brothel, as usual. Relax, brother. You have more important things to worry about. I'll send to look for him - Geta whispered with furrowed brows to his leaning brother, who nervously played with his rings, looking at the whole room with fear. He didn't know any of these people.
It was true that Caracalla was always the first to seek out his father when he was roaming around Rome with a hood covering his face. As has already been mentioned, he chased women. And his son chased after him. He woke him up, led him home, maybe in a way he looked after him, worried about him. Maybe that was why he was so concerned about his father’s every word. Because, after all, he was close to his father.
The Praetorians did not search for long, his father was walking with unsteady steps to the dining hall. When the large doors opened, they revealed a drunken Septimius Severus. Despite everything, the man had a hard head when it came to alcohol. Regardless of his lung disease, he maintained the form of a functioning alcoholic. Coughing mercilessly, he caught everyone's attention, standing exactly on the opposite side of the abundant table. Only a murmur of whispers remained in the hall because no one valued the emperor very much, certainly not as much as his sons. He raised a large, filled goblet.
- You see, you sent him to us - Geta said with embarrassment, raising the wine to his lips, trying to block out the humiliating sight from his field of vision.
- Sons! You are in the prime of life! Grown, handsome, your whole life lays open before you, like the legs of a cheap whore! - The murmurs died down as it seemed that the only thing that could be heard was the father's laughter and the son's gnashing of teeth. - So I have one last fatherly demand. Live in harmony, enrich the soldiers, and apart from that.. You can despise everyone. Just remember... remember the family - the old man's voice trembled uncontrollably because no one took him seriously.
Even the sons hid their faces in their hands, awkwardly glanced to the sides, cursing their father in their thoughts.
Maybe they subconsciously sent what was to happen to him. Severus was dressed in a long black robe, in which he demanded many pockets, so it looked unique and unusual. From one of the pockets by his hip, he pulled out a small sword, bearing small images of Caracalla and Geta as young twins embraced by their mother with her eyes closed. This old man stubbornly clung to his miserable life as a failed emperor, even when he knew that his years of conquest were behind him as if he wanted to fulfill some task. It turned out that the task was his sons and their rule. When it was fulfilled, he went to have one last night of fun, then returned in the morning to say goodbye to his loved ones. He quickly ran the blade across the fold of his neck, from which the soul of the old ruler flew away, whose body then fell onto the rich table, onto the great roast and onto the goblets of wine. People stood up as if scalded, women screamed as if they had been skinned, Emperor Geta stood up to run towards his dead father - and Caracalla, Caracalla was sitting, and in his eyes was smoldering the flame with the embryo of madness, which had been awakened by unbearable pain, the pain of death and everything he had experienced.
@doodle-with-rhy
thank you all so much for your support! Comment if you want a continue
#gladiator 2#gladiator ii#emperor caracalla#emperor geta#general acacius#geta x reader#caracalla x reader#joseph quinn#pedro pascal#fred hechinger#gladiator ii fanfiction#gladiator ii imagine#emperor Caracalla#fanfiction#fanfic#prologue#chapter 1#roman emperors#rome
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Roman Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt
In ancient history the pharaoh was the head of state and ruler of the country. However, he was not just a secular ruler, but a divine being on Earth who acted as an intermediary between the spiritual world and the earthly world. In essence he was a mortal representative of the gods. Interestingly, one did not have to be an Egyptian to be an Egyptian pharaoh. The act of conquering and ruling Egypt qualified one to be a pharaoh. As a result there were many foreign pharaohs throughout Egyptian history including those who were Persian, Nubian, Libyan, Hyksos, Kushite, and Macedonian Greek.
In 30 BC Cleopatra VII became the last ruler of Egypt from the Macedonian Greek Ptolemaic Dynasty. Cleopatra had backed the losing side of a Roman civil war, opposing Octavian and supporting Marc Antony. Octavian won, she was deposed, she committed suicide, and Egypt became a Roman province. When Octavian became Augustus and founded the Roman Empire, the Egyptians also recognized him as the official Pharaoh of Egypt. Afterwards successive Roman emperors were also declared pharaohs, until around the 4th century when Christianity became the dominant religion in Egypt.
Truth be told, most if not all Roman emperors didn't give a damn about being pharaohs. Most emperors never even stepped foot in Egypt and it didn't seem like they took their role as pharaoh very seriously. Regardless Egyptian iconography and art was crafted depicting Roman emperors in Egyptian style wearing Egyptian royal regalia and interacting with Egyptian gods. Some interesting examples are...
Gigachad Pharaoh Augustus
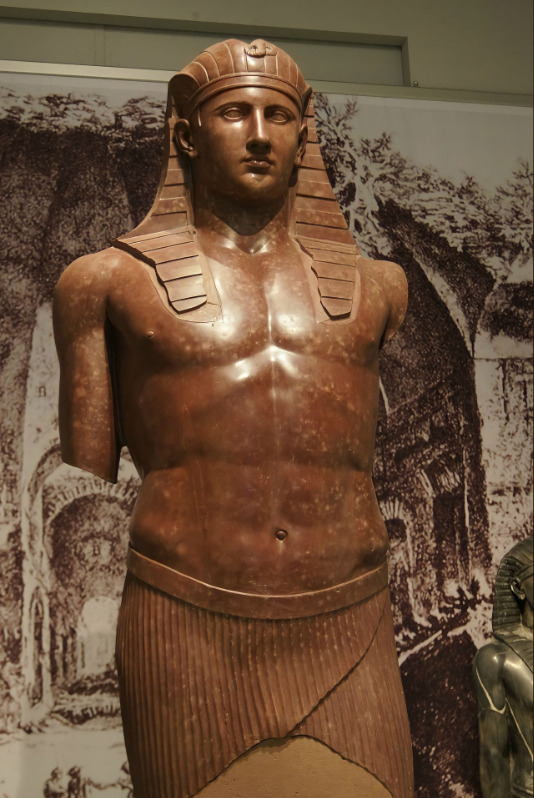

Tiberius

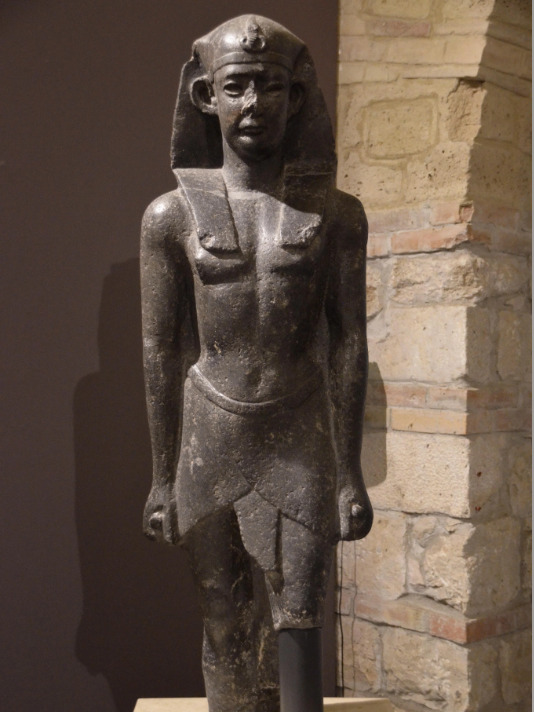
Nero
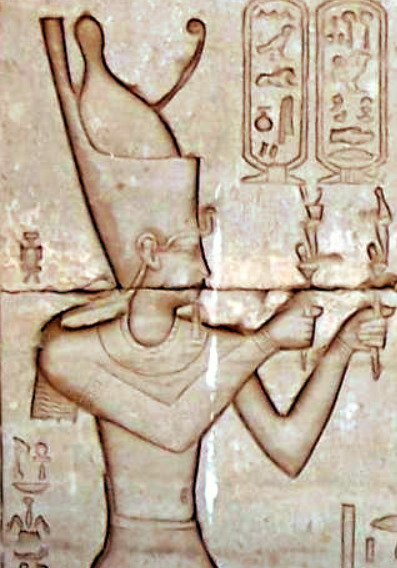
Nero again

Trajan making sacrifices to Hathor

Domitian

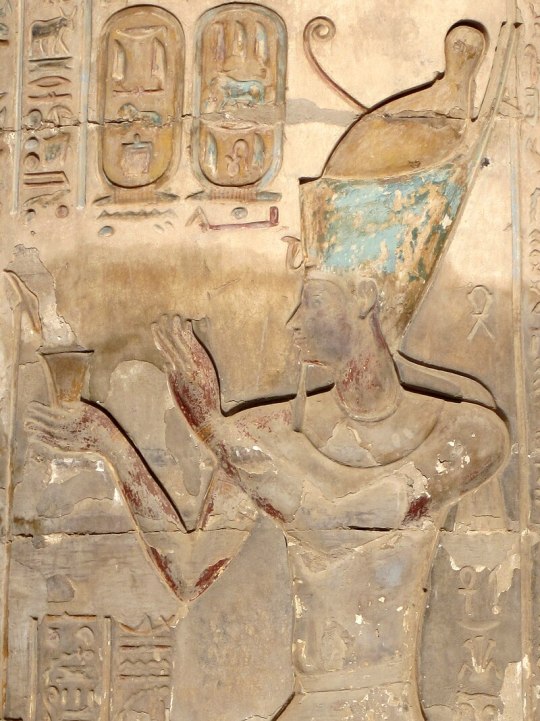
Domitian with Horus
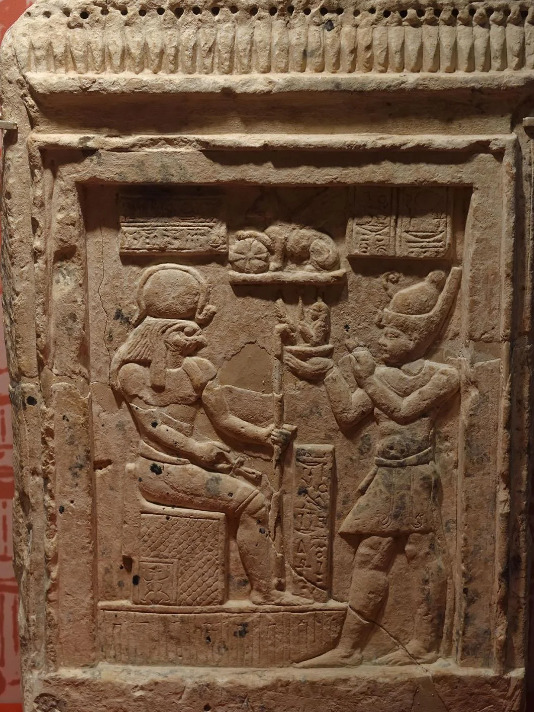

Caracalla
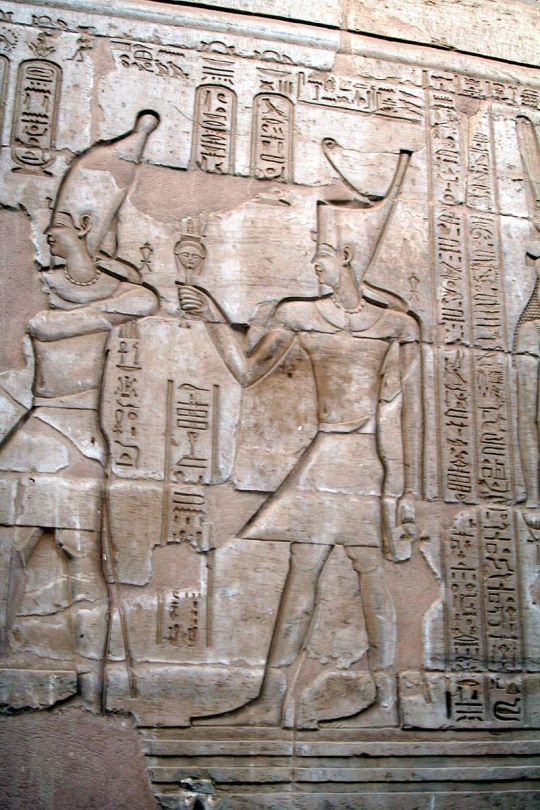

Marcus Aurelius

168 notes
·
View notes
Text

A ROMAN MARBLE PORTRAIT BUST OF THE EMPEROR LUCIUS VERUS ANTONINE PERIOD, LATE 2ND CENTURY A.D.
Lucius Aurelius Verus (15 December 130 – January/February 169) was Roman emperor from 161 until his death in 169, alongside his adoptive brother Marcus Aurelius. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. Verus' succession together with Marcus Aurelius marked the first time that the Roman Empire was ruled by more than one emperor simultaneously, an increasingly common occurrence in the later history of the Empire.
Born on 15 December 130, he was the eldest son of Lucius Aelius Caesar, first adopted son and heir to Hadrian. Raised and educated in Rome, he held several political offices prior to taking the throne. After his biological father's death in 138, he was adopted by Antoninus Pius, who was himself adopted by Hadrian. Hadrian died later that year, and Antoninus Pius succeeded to the throne. Antoninus Pius would rule the empire until 161, when he died, and was succeeded by Marcus Aurelius, who later raised his adoptive brother Verus to co-emperor.
As emperor, the majority of his reign was occupied by his direction of the war with Parthia which ended in Roman victory and some territorial gains. In the spring of 168 war broke out in the Danubian border when the Marcomanni invaded the Roman territory. This war would last until 180, but Verus did not see the end of it. In 168, as Verus and Marcus Aurelius returned to Rome from the field, Verus fell ill with symptoms attributed to food poisoning, dying after a few days (169). However, scholars believe that Verus may have been a victim of smallpox, as he died during a widespread epidemic known as the Antonine Plague.
Despite the minor differences between them, Marcus Aurelius grieved the loss of his adoptive brother. He accompanied the body to Rome, where he offered games to honour his memory. After the funeral, the senate declared Verus divine to be worshipped as Divus Verus.
#A ROMAN MARBLE PORTRAIT BUST OF THE EMPEROR LUCIUS VERUS#ANTONINE PERIOD#LATE 2ND CENTURY A.D.#marble#marble bust#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient rome#roman history#roman empire#roman emperors#roman art
166 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Birth and death locations of Roman Emperors (Augustus to Theodosius), modern borders.
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
Geta, Caracalla x original character.
In the splendor of Rome, under its opulent arches and vibrant murals, a story of twisted obsession unfolded within the walls of the imperial palace. At the heart of this tale were two brothers, Geta and Caracalla, both emperors, bound by blood yet ensnared in a dark rivalry fueled by their infatuation with a slave girl named Rose.
Rose was a delicate blossom amidst the gathering storm—a vision of elegance with her shimmering dark hair and haunting hazel eyes. The twins’ gazes lingered on her like a flame drawn to a moth, each brother yearning for her attention, each driven by desires that simmered just below the surface, blurring the lines of affection and possession.
On this fateful day, they found themselves in the grand amphitheater, surrounded by the raucous cheers of spectators as gladiators fought for glory and survival. Rose sat between them, her heart racing not from excitement but from fear. She clutched her knees tightly to her chest, shielding herself from the violence unfolding before her.
“Look at how strong they are!” Geta exclaimed, feigning enthusiasm as he nudged her shoulder playfully. “Don’t you find it exhilarating, Rose?”
“It’s… terrifying,” she replied softly, her voice barely above the roar of the crowd. She turned her gaze away from the arena, feeling the heat of their stares upon her, a weight she could hardly bear.
Caracalla leaned closer, his breath hot against her ear, “But we shall protect you, sweet Rose. You will never have to fear anything while we are near.” He rested a hand possessively around her waist, drawing her closer, a grip that sent shivers down her spine—of both dread and an undeniable thrill.
Their attention shifted abruptly to an imposing figure entering the arena: a majestic tiger. Its coat glistened under the sun, a living emblem of grace and ferocity. For a moment, Rose felt a flicker of hope, a bond with the creature that mirrored the wildness inside her.
“Look at it, Rose!” Geta urged, a gleam of anticipation in his eyes. “Isn’t it beautiful?”
But as the fight commenced, the tiger’s struggle against its fate broke Rose’s heart. When the gladiator thrust a blade into the magnificent creature, a scream tore from her throat, raw and untempered, cutting through the cheers of the crowd. “No! Stop!”
“Why do you weep?” Caracalla asked, chin tilted upward as he observed her horror with a mix of amusement and intrigue. “It’s just a beast. You don’t want to be part of such a world, do you?”
Rose could only stare, horrified, as the once proud animal fell, its lifeblood staining the sand. She turned away, tears streaming down her cheeks, wishing for the comfort of her own thoughts far away from this brutal reality.
After the spectacle had concluded, the atmosphere shifted. The twins approached her, shadows looming over her fragile form. In their hands, they revealed a luxurious rug—an exquisite tiger skin, expertly crafted, the stripes bold against the smooth fur.
“We wanted you to have something special,” Geta said, pride lacing his voice. “A piece of that magnificent creature. Envision yourself wrapped in its strength.”
“Or perhaps lying on it with us,” Caracalla added, an unsettling smile crossing his lips as he pulled Rose onto his lap, holding her close against him. She felt the weight of his desire pressing down like an iron ball.
As she settled awkwardly, unable to escape the warmth of his embrace, he continued, “We thought the rug would be perfect for our gatherings. Just imagine—life and death intertwined beneath you, with us by your side.”
Rose’s heart raced, caught in a torrent of emotions. The rug was a reminder of both beauty and brutality, and the implications of his words sent chills through her. “It’s too much,” she murmured, fighting back the nausea rising in her throat. “I cannot accept this.”
“Why not?” Geta leaned in, brushing a lock of hair behind her ear, his fingers lingering against her skin. “It is our gift to you, a token of our devotion. With it, you’ll always have the power of the tiger at your disposal.”
As the tension filled the space between them, Rose felt both trapped and strangely compelled. Unspoken dread curled in her stomach as she tried to mask her true feelings, forcing a smile that didn’t quite reach her eyes. “Thank you,” she eventually whispered, almost as if surrendering to their dark enchantment.
“See? She appreciates it,” Caracalla remarked, tightening his hold around her waist. “You’ll come to love it just as we love you.”
The air thickened with their combined desires, suffocating and intoxicating. She could feel the possibilities unfurling around her like the vines of a serpent, coiling tighter with each passing moment. The bond she had hoped to form with the tiger now mirrored the sinister intentions of the brothers who held her captive in their sanctuary of power.
And as night descended on the amphitheater, the shadows deepened, casting their ominous hues over Rose’s fate. In the midst of lavish palaces and grand conquests, the twisted love of two emperors tightened its grip around her heart, leaving her to navigate a realm where loyalty morphed into obsession, and freedom became an elusive dream, forever haunted by the echoes of the arena and the chilling laughter of those who claimed to adore her.
#story#fanfic#gladiator ll#gladiator ii#gladiator 2#gladiator movie#emperor geta#geta x reader#emperor caracalla#caracalla x reader#original character#roman emperors#x original character#possesive love#obsessive love#gladiator geta#gladiator caracalla
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gladiator Movie Aesthetic
#gladiator#maximus#maximus decimus meridius#roman legion#roman soldiers#roman emperors#roman empire#marcus aurelius#commodus#rome#ancient rome#spaniard#coloseum#colosseum#colosseo#roma#now we are free#movies#films#gladiator movie#russel crowe#joaquin phoenix#richard harris#movie aesthetic#film aesthetic#aesthetic#movie edit#film edit#roman era#roman military
102 notes
·
View notes
Text

"bow to me, Hadrian, your favourite Roman emperor" like what a notification to suddenly get from the chess.com app, I guess this is how they try to get me back and yes it might be working...
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
ANCIENT ROME FAMILY TREES !!
(that I've written down so far)
- THE JULIOCLAUDIANS (until Claudius, sorry Nero! - starting from Brutus' ancestors)

- MARCELLUS AND HIS FAMILY (down to Messalina!)

- THE FAMILY OF AELIUS SEJANUS (the only one whose family isn't a circle)

#absolute insanity#silly#family trees#marcus junius brutus#ancient rome#roman empire#roman republic#julio claudian dynasty#octavian#augustus#lucius aelius sejanus#caligula#i lost my mind#valeria messalina#tiberius#roman emperors#julia the elder#agrippa#agrippina#uhhhhhhh#will update more#PLEASE i sweat and lost my neurons over this#cato the younger#:3#ides of march#julius caesar
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
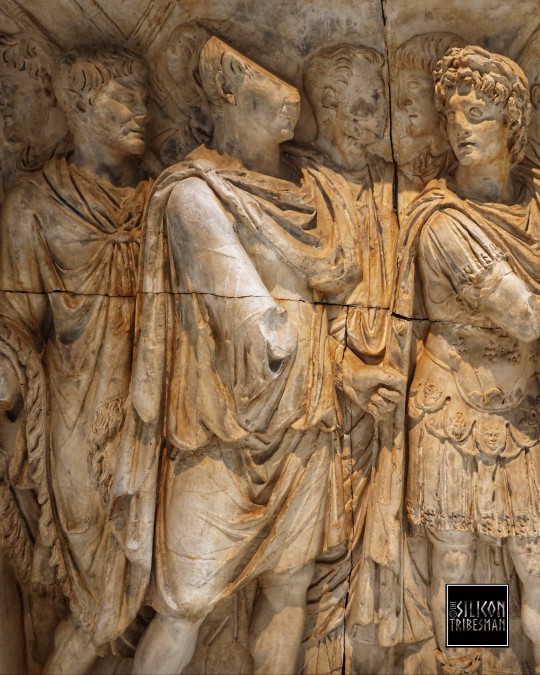






Trajan Recruits Soldiers. Arch of Trajan at Beneventum, 114 CE
A cuirassed military god in the centre presents a recruit to the roman emperor. The new soldier stands feet together: his height is being measured by a wooden frame held by the soldier on the right (in situ, west side, middle zone)
Ashmolean Museum, Oxford
#roman#romans#roman empire#roman army#roman soldiers#roman sculpture#roman craft#roman statue#roman society#trajan#ashmolean#archaeology#relic#ancient cultures#roman emperors
244 notes
·
View notes
Text
Optimus princeps

Marcus Ulpius Trajan was born on 18 September 53 in Hispania Baetica ( Andalusia, Spain) in the ancient city Italica. He stood out for his military and political brilliance, his uprightness and fight against corruption, his austere character, and his philanthropy.
He was the only Roman emperor to whom he granted the title Optimus (The Best). With him the so-called Golden Age of the Roman Empire began. With him also began the so-called era of provincial emperors.
Trajan created Institutio Alimentaria, a program that helped orphaned and poor children throughout the Roman Empire. It provided food and subsidized education.
He conquered Dacia (Roman Dacia would evolve over time to give rise to present-day Romania) and defeated the Parthian Empire by conquering vast territories. During his reign the Roman Empire reached its maximum extension, setting its eastern border on the Tigris River and not on the Euphrates as it was before Trajan.
Trajan is mentioned in The Romanian National Anthem. In Romania the name TRAIAN is very common.
He was the only Roman emperor, before Constantine, who was held in high esteem in medieval and Renaissance Christian Europe, even though under his reign Christianity was prohibited (but without bloody persecutions).
Trajan was the last conqueror of Rome; his nephew and successor Hadrian marked the definitive borders of the empire.
"Be more fortunate than Augustus and better than Trajan" It became the greeting to emperors

Trajan spent his childhood during the reign of Nero. At the age of 15 he experienced the first civil war of the imperial era and the year of the 4 emperors. He made a career in the army under the principate of Vespasian and his sons Titus and Domitian; Was close and loyal to the Flavian Dynasty.
Following the assassination of Domitian in September 96, Nerva was proclaimed emperor.
In 97 a revolt by members of the Praetorian Guard forced the elderly and childless Nerva to adopt as his heir and successor the popular Trajan, then governor of Germania Superior.
Nerva died on 28 January 98 and Trajan succeeded him. One of his first acts was the construction of a limes to secure the Decuman Fields, Germanic lands on the right side of the Rhine, which had been won under Domitian.
Trajan arrived in Rome two years after being proclaimed emperor, having secured the Rhenish frontier. He was received with great joy.

Trajan's Forum in Rome was built by the architect Apollodorus of Damascus, chosen by Trajan himself. It included a basilica, two libraries, and after Trajan's death, a temple was built in his honour. Trajan's Column is the only structure that has survived.


The column was inaugurated on May 12, 113 and consists of a long spiral frieze describing the Dacian Wars (101-106)

The Alcántara Bridge, Extremadura, Spain, widely regarded as a masterpiece of Roman engineering, was built during the reign of Trajan. Photo: Dantla from de.wikipedia - Own work, GFDL


His wife Pompeia Plotina. Ph: Carole Raddato. And his niece Salonia Matidia. Ph: Louvre Museum , CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Trajan was married to Pompeia Plotina, who according to Pliny the Younger "Added to Trajan's virtues of modesty and nobility of spirit her own, for she was kind, intellectual and benevolent."
They had no offspring but Trajan had a single niece, Salonia Matidia, whom he and his wife loved as a daughter and in fact she lived with them since she was 10 years old when her father died.
This lady is the key to understanding how Trajan's successors, supposedly adopted by choice only for their qualities, are linked by blood or marriage ties related to Salonia Matidia. In the so-called "Antonine Dynasty" (name given by 18th century European historians) or dynasty of the "adoptive Emperors" all except Nerva were related to each other and to Trajan through women, either through collateral kinship, marriage or both.
Ulpius-Aelia is the correct name for the dynasty that begins with Trajan and ends with Commodus. And in the list of the "five good emperors" modern historians should eliminate Nerva, who did nothing good - and appointed Trajan as his successor under duress - and include instead Lucius Verus, co-emperor with Marcus Aurelius, who ruled for eight years and was a good ruler.

Trajan died of illness between 8 / 9 August 117 in Selinus (Cilicia). His wife placed the urn containing his ashes on Trajan's Column. He was deified by the Senate.

Trajan's Column, Rome. Photo: Nikon Z7II, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Trajan's Column was an absolute novelty in ancient art and became the most avant-garde work of Roman historical relief.
68 notes
·
View notes
Text

As it should be.
#ides of march#julius caesar#tumblr traditions#tumblr#social media#roman empire#roman emperors#et tu brute#et tu brutus?
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy Ides of March! Do not forget to stab your nearest authoritarian politician.
#ides of march#julius caesar#stabbing#ancient rome#rome#ceaser#we gonna go stabbieeee#roman emperors#dictators#knives
83 notes
·
View notes